Sox Iso 27001 Mapping A Drive
Network Mapping Management Taxonomy. ISO/IEC 27001 ISO/IEC 27002 HITRUST. SOX 404 NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 4 FFIEC HITRUST ISO/IEC 27002. I am student of Computer Engineering and I am developing my FPC. This is about making a plan for implementation of COBIT 5 on a real company. Choosing COBIT 5 was due to the company must comply with Sarbanes-Oxley. How can ISO 27001 help you comply with SOX section 404. In the wake of these scandals, U.S. SOX law was introduced to restore public confidence of financial information released by public organizations. The laws required new levels of commitment by organizations’ top management regarding the handling of information, including more severe penalties for fraudulent financial activity.
Compliance will significantly impact the IT organization of most public companies. However, there is one enormous problem: there is no specific mention of IT in Section 404, and more importantly, there are no specifics as to what controls have to be established within an IT organization to comply with Sarbanes-Oxley legislation. If there is no specific mention in Section 404 as to what IT needs to do to comply with Sarbanes-Oxley, the logical question would be,'How can I comply with something without knowing what I need to do to comply?'
Although there are various standards a company can use for defining and documenting its internal controls - ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library), Six Sigma, and COBIT - the majority of auditors have. ITIL is an international series of documents used to aid the implementation of a framework for IT Service Management.The intent of the framework is to define how Service Management is applied within specific organizations. Grand theft auto v free.

Given that the framework consists of guidelines, it is agnostic of any application or platform and can therefore be applied in any organization. Sarbanes-Oxley IT Compliance Using COBIT and Open Source Tools By Christian Lahti, Roderick Peterson, Steve Lanza 356 Pages; $49.95 In many organizations, Six Sigma simply means a measure of quality that strives for near perfection.
Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects (driving toward six standard deviations between the mean and the nearest specification limit) in any process—from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service. COBIT stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology. While the have been around since 1996, the guidelines and best practices have almost become the de facto standard for auditors and SOX compliance, mostly because the COBIT standards are platform independent.
There are approximately 300 generic COBIT objectives, grouped under six COBIT Components. When reviewing and applying the COBIT guidelines and best practices, keep in mind that they will need to be tailored to your particular environment.
The six COBIT components COBIT consists of six components:. Executive Summary Explains the key concepts and principles. Framework Foundation for approach and COBIT elements.
Organizes the process model into four domains: - Plan and organize - Acquire and implement - Deliver and support - Monitor and evaluate. Control Objective Foundation for approach and COBIT elements. Organizes the process model into the four domains (discussed in a moment). Control Practices Identifies best practices and describes requirements for specific controls. Management Guidelines Links business and IT objectives and provides tools to improve IT performance.
Audit Guidelines Provides guidance on how to evaluate controls, assess compliance and document risk with these characteristics: - Define 'internal controls' over financial reporting - Internally test and assess these controls - Support external audits of controls - Document compliance efforts - Report any significant deficiencies or material weaknesses In conclusion, although an IT organization is free to select any predefined standards, or even one they develop to assist them in obtaining Sarbanes-Oxley compliance, the mostly widely accepted standard is COBIT. Subsequently, you may find that selecting COBIT will be the path of least resistance to Sarbanes-Oxley compliance. Read the rest of, SOX and COBIT defined.
Introduction to the Cloud Controls Matrix Working Group The Cloud Security Alliance Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) is specifically designed to provide fundamental security principles to guide cloud vendors and to assist prospective cloud customers in assessing the overall security risk of a cloud provider. The CSA CCM provides a controls framework that gives detailed understanding of security concepts and principles that are aligned to the Cloud Security Alliance guidance in 13 domains.
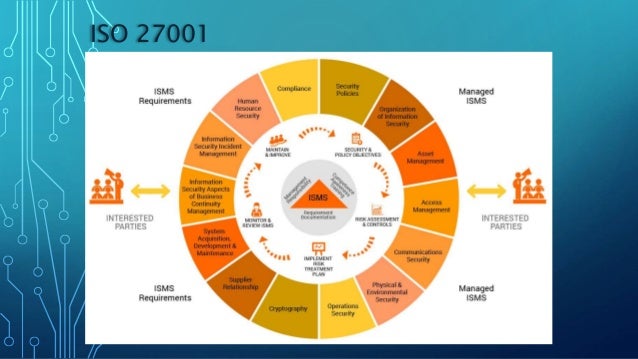
What Is Iso 27001 Certification
The foundations of the Cloud Security Alliance Controls Matrix rest on its customized relationship to other industry-accepted security standards, regulations, and controls frameworks such as the ISO 2, ISACA COBIT, PCI, NIST, Jericho Forum and NERC CIP and will augment or provide internal control direction for service organization control reports attestations provided by cloud providers. As a framework, the CSA CCM provides organizations with the needed structure, detail and clarity relating to information security tailored to the cloud industry. The CSA CCM strengthens existing information security control environments by emphasizing business information security control requirements, reduces and identifies consistent security threats and vulnerabilities in the cloud, provides standardized security and operational risk management, and seeks to normalize security expectations, cloud taxonomy and terminology, and security measures implemented in the cloud. Download the Cloud Controls Matrix Version 3 Document Version Release Date Download Cloud Controls Matrix 3 About CCM v3 The CSA Cloud Control Matrix (CCM) Version 3.0, is a comprehensive update to the industry’s gold standard for assessing cloud centric information security risks. The CCM Version 3.0 expands its control domains to address changes in cloud security risks since the release of the CSA’s seminal guidance domain, “Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing version 3.0” while making strides towards closer harmonization of the two. Having drawn from industry-accepted security standards, regulations, and control frameworks such as ISO 27001/2, the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security (ENISA) Information Assurance Framework, ISACA’s Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology, the American Institute of CPAs Trust Service and Principals Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, and the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program, the updated CSA CCM control domain provides organizations with the cohesiveness of controls needed to manage cloud centric information security risks.
This major restructuring of the CCM also captures the needs of cloud security governance in the near future, where it will serve as an annual check in updating future controls, further ensuring CCM remains in line with future technology and policy changes. Download the Cloud Controls Matrix Version 1.4 Document Version Release Date Download Cloud Controls Matrix 1.4 About CCM v1.4 Version 1.4 of the Cloud Controls Matrix includes two new mapping columns relating to AICPA’s SOC 2 engagement. The SOC 2 report provides cloud service organizations and cloud users more flexibility related to compliance and operational reporting controls.
It addresses risk of IT-enabled systems and privacy programs beyond the controls necessary for financial reporting. Cloud Controls Matrix V1.4 Contributors Working Group Co-Chair(s) CSA Global Support Control Area Mapping Leads.
Evelyn de Souza. Sean Cordero. Thomas Kenyon. J.R. Santos.
John Yeoh. Audrey Katcher. Chris Halterman. Janis Parthun.
Erin Mackler About AICPA The AICPA is the world’s largest member association representing the accounting profession, with nearly 386,000 members in 128 countries and a 125-year heritage of serving the public interest. AICPA members represent many areas of practice, including business and industry, public practice, government, education and consulting. The AICPA sets ethical standards for the profession and U.S. Auditing standards for audits of private companies, nonprofit organizations, federal, state and local governments.
It develops and grades the Uniform CPA Examination and offers specialty credentials for CPAs who concentrate on personal financial planning; fraud and forensics; business valuation; and information technology. Through a joint venture with the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, it has established the Chartered Global Management Accountant designation to elevate management accounting globally. Download the Cloud Controls Matrix Version 1.3 Document Version Release Date Download Cloud Controls Matrix 1.3 Cloud Controls Matrix V1.3 Contributors Working Group Co-Chair(s) CSA Global Support Control Area Mapping Leads. Becky Swain.
Evelyn de Souza. Sean Cordero. Thomas Kenyon. J.R. Santos.
John Yeoh. Balaji Ramamoorthy. Chris Davis. Daniel Philpott. David Lingenfelter.
Doug Barbin. Evelyn de Souza. Matthew Metheny. The Late Ron Knode. Tim Mather About FedRAMP The Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) is a US government-wide mandated program that provides a standardized approach to security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for cloud products and services. This approach uses a “do once, use many times” framework that is intended to save cost, time, and staff required to conduct redundant agency security assessments. There are no “new” controls for FedRAMP.
The FedRAMP security controls are based on NIST SP 800-53 R3 controls for low and moderate impact systems and contain controls and enhancements above the NIST baseline for low and moderate impact systems that address the unique elements of cloud computing. For additional information, refer to the FedRAMP FAQ website located at:. Authoritative Source.
CSA CCM R1.1 – PCI DSS v2.0. Pritam Bankar, CISA, CISM – Infosys Technologies Ltd. (Lead). Karthik Amrutesh, CISSP, CISA – Ernst and Young LLP. Chris Brenton – Dell.
Dr. Anton Chuvakin – Security Warrior Consulting. Michael Craigue, Ph.D. (CISSP, CSSLP) – Dell.
Jakob Holm Hansen, CISA, CISSP, ABCP – Neupart A/S. Addison Lawrence – Dell. Steve Primost, CISSP, CISM. Philip Richardson, CISSP, A.Inst.ISP, MBCS – Logicalis UK Ltd. Paul Stephen – Ernst and Young LLP CSA CCM R1.1 – BITS Shared Assessment AUP v5.0 / SIG v6.0. Niall Browne, CCSP, CISA, CISSP, CCSI – LiveOps.
Henry Ojo – Kamhen Services Ltd, HISPI CSA CCM R1.1 – GAPP. Thej Mehta, CISA, ITIL v3 Foundation, ISACA San Francisco Chapter: 2nd Vice President and Education Program Chair, KPMG LLP (Lead). Pritam Bankar, CISA, CISM – Infosys Technologies Ltd. Thomas Loczewski – Ernst and Young LLP. Lloyd Wilkerson – Robert Half International. Anna Tang, CISSP, CIPP, CIPP/IT, Cisco Systems, Inc. CSA CCM R1.1 – QA Team.
John DiMaria – HISPI (Lead). Taiye Lambo – eFortresses, Inc, HISPI. Kelvin Arcelay, CISM, CISSP, CRISC, HISP, ISMS Auditor, PMP, SSGB – Arcelay & Associates, HISPI. Henry Ojo – Kamhen Services Ltd, HISPI. Lisa Peterson, CISA, CISSP – Progressive Insurance, HISPI. Dale Pound – SAIC, HISPI. John Sapp – McKesson Healthcare, HISPI.
Gary Sheehan – Advanced Server Management Group, Inc., HISPI. Greg Zimmerman – Jefferson Wells, HISPI. Sean Cordero Sean Cordero brings more than 15 years of information security and IT experience to his current role as director, information security at Optiv.
Cordero provides executive level advisement for the company’s Fortune 50 clients. Cordero’s prior leadership roles included: President of Cloud Watchmen, CSO for EdFund, CSO for ECMC West, Director of Security and Compliance for Charlotte Russe. Cordero is a thought-leader and serves as chair of the Cloud Security Alliance’s (CSA) Cloud Control Matrix working group where he drives the development of security standards for cloud computing. Cordero was awarded the 2013 Ron Knode Service Award by the Cloud Security Alliance for his contributions to cloud research.
Cordero is active in the conference speaking circuit where he has presented for CSO magazine, the CSA, the High Technology Crimes Association, Secure360, the University of California, Bsides, and ISACA. Cordero is CISSP, CRISC, CISM and CISA. Contributions: Evangelized use of CCM and the CSA Security, Trust and Assurance Registry (STAR) across the industry at conferences, webinars and podcasts.
Co-led the development of the CCM and helped drive CCM versions 1.3, 1.4, and 3.0. Recipient of 2013 Ron Knode Award.